Age, Biography and Wiki
| Who is it? | Physicist |
| Birth Day | May 19, 1918 |
| Birth Place | Amsterdam, United States |
| Age | 102 YEARS OLD |
| Died On | July 28, 2000(2000-07-28) (aged 82)\nCopenhagen, Denmark |
| Birth Sign | Gemini |
| Residence | Netherlands, United States, Denmark |
| Alma mater | University of Amsterdam, University of Utrecht |
| Known for | G-parity Treatment of SU(6) symmetry breaking Coining the term "Standard Model" |
| Spouse(s) | Jeanne Lila Lee Atwill Ida Nicolaisen |
| Awards | Andrew Gemant Award (1993) |
| Fields | Physicist |
| Institutions | Rockefeller University Institute for Advanced Study, Princeton Niels Bohr Institute |
| Doctoral advisor | Léon Rosenfeld |
Net worth: $800,000 (2024)
Abraham Pais, a renowned physicist in the United States, is estimated to have a net worth of $800,000 in the year 2024. Known for his significant contributions to the field of physics, Pais has made a name for himself through his extensive research and scientific publications. He is highly respected for his work on the theory of elementary particles, and his collaborations with eminent physicists like Albert Einstein and Niels Bohr have greatly influenced the understanding of quantum mechanics. Despite his intellectual feats, Abraham Pais remains a humble and dedicated scientist, whose net worth is a testament to his remarkable achievements in the realm of physics.
Biography/Timeline
Pais was born in Amsterdam, the first child of middle-class Dutch Jewish parents. His father, Isaiah "Jacques" Pais, was the descendant of Sephardic Jews who migrated from Portugal to the Low Countries around the beginning of the 17th century. His mother, Kaatje "Cato" van Kleeff, was the daughter of an Ashkenazi Diamond cutter. His parents met while studying to become elementary-school teachers. They both taught school until his mother quit when they married on December 2, 1916. His only sibling, Annie, was born on November 1, 1920. During Pais's childhood his father was an elementary schoolmaster, headmaster, and later the headmaster of the Sephardic Hebrew school.
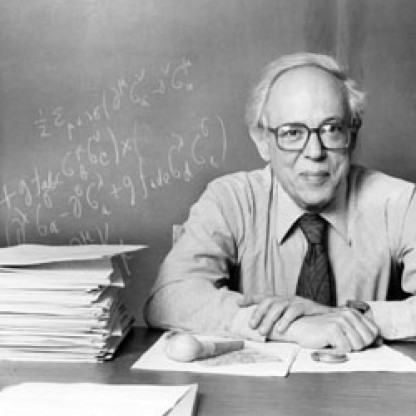
Abraham Pais (/peɪs/; May 19, 1918 – July 28, 2000) was a Dutch-born American Physicist and science Historian. Pais earned his Ph.D. from University of Utrecht just prior to a Nazi ban on Jewish participation in Dutch universities during World War II. When the Nazis began the forced relocation of Dutch Jews, he went into hiding, but was later arrested and saved only by the end of the war. He then served as an assistant to Niels Bohr in Denmark and was later a colleague of Albert Einstein at the Institute for Advanced Study in Princeton, New Jersey. Pais wrote books documenting the lives of these two great physicists and the contributions they and others made to modern physics. He was a physics professor at Rockefeller University until his retirement.
In the fall of 1935 Pais began his studies at the University of Amsterdam without a clear idea regarding his desired career. With an interest in the exact sciences, he gradually gravitated to chemistry and physics as major subjects, and mathematics and astronomy as minor subjects. In the winter of 1936/1937 his career goals were defined by two guest lectures by George Uhlenbeck, professor of theoretical physics at University of Utrecht. Pais was fascinated by Uhlenbeck's discussion of Enrico Fermi's incorporation of the neutrino into the theory of beta radiation.
In the fall of 1938 Pais enrolled for graduate classes at University of Utrecht. Uhlenbeck, however, spent that term as a visiting professor at Columbia University in New York City. He left Pais with the use of his laboratory and a list of topics to study and work on. Pais was soon exposed to other prominent Dutch physicists and areas of research in experimental physics. He became well-acquainted with Hendrik Casimir, a physics professor at Leiden University who lectured at Utrecht twice a week on quantum physics. When Uhlenbeck returned from America, he brought news of a meeting he had attended in Washington, D.C., in which Niels Bohr and Enrico Fermi had first made public their news about nuclear fission. Uhlenbeck also announced that he would be leaving in the summer of 1939 for a professorship at University of Michigan, Ann Arbor.
In the fall of 1939 Pais dedicated himself to preparing for his master's degree. Utrecht experimental Physicist Leonard Salomon Ornstein provided him guidance in his independent physics studies. Uhlenbeck, in anticipation of his departure, introduced Pais to Physicist Hendrik Anthony Kramers at Leiden University, who became his mentor and friend. He was also influenced then by discussions with Léon Rosenfeld of the University of Liège, who was invited to Utrecht to give a colloquium in an effort to find a successor for Uhlenbeck and reported on the work he was then doing with Christian Møller on the meson theory of nuclear forces.
Pais successfully passed the examination for his master's degree on April 22, 1940. On May 7 the Dutch minister of education appointed Rosenfeld to succeed Uhlenbeck at the University of Utrecht. On May 8 Pais wrote to Rosenfeld at Liège to ask if he might continue his studies under him if his appointment came through, and again on May 9 to congratulate him on his appointment. On May 10, 1940, the Germans invaded the Netherlands, Belgium, and Luxembourg, disrupting the mail between Utrecht and Liège for months.
In November 1940 the German authorities issued a decree banning Jews from all civil Service positions, including academic posts. Pais therefore lost his assistant professorship, though Rosenfeld secretly arranged for his successor to unofficially share the responsibilities and salary of the position with Pais. Professor Leonard Ornstein, however, lost his directorship of and access to the laboratory and died a broken man on May 20, 1941. A subsequent German decree ordered that doctorate degrees could not be issued to Jews after June 14, 1941. Pais worked feverishly to complete his dissertation and meet other requirements for his doctorate. He obtained his doctoral degree in theoretical physics on June 9, just five days before the deadline. His was the last Ph.D. issued to a Dutch Jew until after the war.
The Germans began to gradually restrict the activities of the Dutch Jews and in early 1942 required them to wear yellow stars. At first Pais felt safe because his former university status exempted him from being sent to a labor camp. In early 1943, however, the Dutch secretary general of internal affairs, Frederiks, made arrangements for the university Jews to report to Barneveld for their own safety, where they would be housed in a chateau. Pais did not trust that and instead went into hiding. Those who reported to Barneveld were later sent to the Theresienstadt concentration camp where most of them did survive.
His last hiding place was in an apartment with his university friend Lion Nordheim, his wife Jeanne, and her sister Trusha van Amerongen. In the course of his hiding he kept in touch with the scientific community through visits at his hiding place by Hendrik Anthony Kramers and Lambertus Broer. Jeanne and Trusha had blond hair and blue eyes and ventured out in public as non-Jews, while Lion and Pais hid in the apartment. In March 1945, however, they were betrayed and all four were arrested. The same week the Americans had crossed the Rhine and cut the rail lines, making impossible their transfer to a concentration camp. The women were soon released. After a month of interrogation by the Gestapo, Pais was released several days before the end of the war. Nordheim was executed ten days before the end of the war.
During World War II, Pais's doctoral dissertation had attracted the attention of Niels Bohr, who invited him to come to Denmark as his assistant. Pais was forced into hiding before he could leave the Netherlands. In 1946, following the war, Pais was able to accept that invitation and served as a personal assistant to Bohr at his country home in Tisvilde for a year.
In 1947 he accepted a position at the Institute for Advanced Study in the United States and thus became a colleague of Albert Einstein.
In 1949 he became corresponding member of the Royal Netherlands Academy of Arts and Sciences.
He is primarily associated with two concepts that directly contributed to major breakthroughs in his field. The first was the idea of "associated production" to explain the puzzling properties of strange particles. His ideas and those of Murray Gell-Mann resulted in the idea of a quantum number called strangeness. The second concept was Pais's and Gell-Mann's theory regarding the composition of the neutral kaons, proposing that the observed states were admixtures of particles and antiparticles, having different lifetimes; this was experimentally confirmed in the following year by Lederman and collaborators. In 1956, Pais became a naturalized citizen of the United States.
In 1963 Pais accepted a position at Rockefeller University to head the theoretical physics group while Rockefeller was in transition from being a medical institute to a university. He finished his career there as the Detlev W. Bronk professor emeritus.
In the late 1970s Pais became interested in documenting the history of modern physics. He felt he was in a unique position to do so, having known many of the key people and with his knowledge of the language, culture, and science.
In 1979, Pais was awarded the J. Robert Oppenheimer Memorial Prize.
His Inward Bound: Of matter and forces in the physical world (Clarendon Press/Oxford University Press, 1988) describes the events in physics during the preceding 100 years, and tries to explain why they happened as they did.
In 1991 he published Niels Bohr's Times: In physics, philosophy, and polity (Clarendon Press/Oxford University Press, 1991) which describes the life and scientific contributions of Bohr.
In 1995 he teamed with Laurie M. Brown and Sir Brian Pippard to compile a three-volume reference collection of articles portraying the scientific and cultural development of modern physics in Twentieth Century Physics (American Institute of Physics and the Institute of Physics, U.K., 1995). That same year Rockefeller University awarded him the Lewis Thomas Prize for Writing about Science.
A Tale of Two Continents: A physicist's life in a turbulent world (Princeton University Press, 1997) was his autobiography. It refers to the 'esemplastic power of the imagination'.
His book The Genius of Science: A portrait gallery (Oxford University Press, 2000) contains biographies of seventeen distinguished physicists he had known personally: Niels Bohr, Max Born, Paul Dirac, Albert Einstein, Mitchell Feigenbaum, Res Jost, Oskar Klein, Hans Kramers, Tsung-Dao Lee and Chen Ning Yang, John von Neumann, Wolfgang Pauli, Isidor Isaac Rabi, Robert Serber, George Uhlenbeck, Victor Frederick Weisskopf, and Eugene Wigner.
The American Physical Society has awarded an Abraham Pais Prize for History of Physics annually since 2005.
Pais was working on a biography of Robert Oppenheimer at the time of his death. It was finished by Robert P. Crease and published posthumously as J. Robert Oppenheimer: A life (Oxford University Press, 2006). It is the most complete biography of Oppenheimer to date.
Pais was perhaps best known for his biography of Albert Einstein, "Subtle is the Lord—": The science and the life of Albert Einstein (Oxford University Press, 1982), and its sequel, Einstein Lived Here (Clarendon Press/Oxford University Press, 1994). "Subtle is the Lord—" won the 1983 U.S. National Book Award in Science.