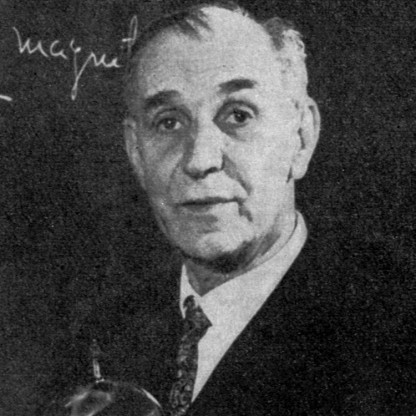Age, Biography and Wiki
| Who is it? | Physicist |
| Birth Day | May 03, 1902 |
| Birth Place | Guebwiller, Alsace, German Empire, French |
| Age | 118 YEARS OLD |
| Died On | 7 January 1984 (aged 81)\nBandol, France |
| Birth Sign | Gemini |
| Alma mater | École Normale Supérieure, University of Paris |
| Known for | Optical pumping technique |
| Awards | Holweck Prize (1954), CNRS Gold medal (1964), Nobel Prize for Physics (1966) |
| Fields | physics |
| Doctoral advisor | Pierre Daure (fr) |
| Doctoral students | Claude Cohen Tannoudji |
Net worth: $10 Million (2024)
Alfred Kastler, a renowned French physicist, has an estimated net worth of $10 million in 2024. Kastler is highly regarded for his significant contributions in the field of physics, particularly in the study of optical pumping and the development of the technique of optical pumping spectroscopy. His groundbreaking work earned him the prestigious Nobel Prize in Physics in 1966. Throughout his career, Kastler has made numerous scientific breakthroughs and conducted extensive research, solidifying his position as one of the most influential physicists of his time. With his wealth and profound knowledge, Kastler has undoubtedly left an indelible mark on the scientific community.
Biography/Timeline
Kastler was born in Guebwiller (Alsace, German Empire) and later attended the Lycée Bartholdi in Colmar, Alsace, and École Normale Supérieure in Paris in 1921. After his studies, in 1926 he began teaching physics at the Lycée of Mulhouse, and then taught at the University of Bordeaux, where he was a university professor until 1941. Georges Bruhat asked him to come back to the École Normale Supérieure, where he finally obtained a chair in 1952.
He won the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1966 "for the discovery and development of optical methods for studying Hertzian resonances in atoms".
In 1978 he became foreign member of the Royal Netherlands Academy of Arts and Sciences.
In 1979, Kastler was awarded the Wilhelm Exner Medal.
Professor Kastler died on 7 January 1984, in Bandol, France.
Over the forty years that followed, this group has trained many of young physicists and had a significant impact on the development of the science of atomic physics in France. The Laboratoire de Spectroscopie hertzienne has then been renamed Laboratoire Kastler-Brossel in 1994 and has got a part of its laboratory in Université Pierre et Marie Curie mainly at the École Normale Supérieure.