Age, Biography and Wiki
| Who is it? | Physicist |
| Birth Day | February 12, 1918 |
| Birth Place | New York City, United States |
| Age | 102 YEARS OLD |
| Died On | July 16, 1994(1994-07-16) (aged 76)\nLos Angeles, California, U.S. |
| Birth Sign | Pisces |
| Alma mater | City College of New York Columbia University |
| Known for | Quantum electrodynamics Spin–statistics theorem Sigma model MacMahon Master theorem List of things named after Julian Schwinger |
| Spouse(s) | Clarice Carrol (m. 1947) |
| Awards | Albert Einstein Award (1951) National Medal of Science (1964) Nobel Prize in Physics (1965) |
| Fields | Physics |
| Institutions | University of California, Berkeley Purdue University Massachusetts Institute of Technology Harvard University University of California, Los Angeles |
| Doctoral advisor | Isidor Isaac Rabi |
| Doctoral students | Roy Glauber Ben R. Mottelson Sheldon Lee Glashow Walter Kohn Bryce DeWitt Daniel Kleitman Sam Edwards Gordon Baym Lowell S. Brown Stanley Deser Lawrence Paul Horwitz Margaret G. Kivelson |
Net worth
Julian Schwinger, renowned physicist in the United States, is projected to have a net worth ranging from $100K to $1M in the year 2024. As one of the leading figures in the field of quantum electrodynamics, Schwinger made pioneering contributions to our understanding of the fundamental forces of nature. His groundbreaking work earned him numerous accolades, including the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1965. Despite his remarkable achievements, Schwinger's estimated net worth reflects the modest financial rewards often associated with the pursuit of scientific research and academic pursuits.
Biography/Timeline
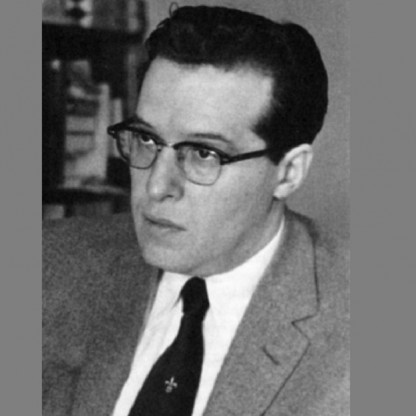
Julian Seymour Schwinger was born in New York City, to Jewish parents originally from Poland, Belle (née Rosenfeld) and Benjamin Schwinger, a garment manufacturer, who had migrated to America. Both his father and his mother's parents were prosperous clothing manufacturers, although the family Business declined after the Wall Street Crash of 1929. The family followed the Orthodox Jewish tradition. He attended Townsend Harris High School and then the City College of New York as an undergraduate before transferring to Columbia University, where he received his B.A. in 1936 and his Ph.D. (overseen by Isidor Isaac Rabi) in 1939 at the age of 21. He worked at the University of California, Berkeley (under J. Robert Oppenheimer), and was later appointed to a position at Purdue University.
After having worked with Oppenheimer, Schwinger's first regular academic appointment was at Purdue University in 1941. While on leave from Purdue, he worked at the Radiation Laboratory at MIT instead of at the Los Alamos National Laboratory during World War II. He provided theoretical support for the development of radar. After the war, Schwinger left Purdue for Harvard University, where he taught from 1945 to 1974. In 1966 he became the Eugene Higgins professor of physics at Harvard.
In the 1960s, Schwinger formulated and analyzed what is now known as the Schwinger model, quantum electrodynamics in one space and one time dimension, the first Example of a confining theory. He was also the first to suggest an electroweak gauge theory, an SU(2) gauge group spontaneously broken to electromagnetic U(1) at long distances. This was extended by his student Sheldon Glashow into the accepted pattern of electroweak unification. He attempted to formulate a theory of quantum electrodynamics with point magnetic monopoles, a program which met with limited success because monopoles are strongly interacting when the quantum of charge is small.
Schwinger was jointly awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1965 for his work on quantum electrodynamics (QED), along with Richard Feynman and Shin'ichirō Tomonaga. Schwinger's awards and honors were numerous even before his Nobel win. They include the first Albert Einstein Award (1951), the U.S. National Medal of Science (1964), honorary D.Sc. degrees from Purdue University (1961) and Harvard University (1962), and the Nature of Light Award of the U.S. National Academy of Sciences (1949).
Schwinger had a mixed relationship with his colleagues, because he always pursued independent research, different from mainstream fashion. In particular, Schwinger developed the source theory, a phenomenological theory for the physics of elementary particles, which is a predecessor of the modern effective field theory. It treats quantum fields as long-distance phenomena and uses auxiliary 'sources' that resemble currents in classical field theories. The source theory is a mathematically consistent field theory with clearly derived phenomenological results. The criticisms by his Harvard colleagues led Schwinger to leave the faculty in 1972 for UCLA. It is a story widely told that Steven Weinberg, who inherited Schwinger's paneled office in Lyman Laboratory, there found a pair of old shoes, with the implied message, "think you can fill these?". At UCLA, and for the rest of his career, Schwinger continued to develop the source theory and its various applications.
After 1989 Schwinger took a keen interest in the non-mainstream research of cold fusion. He wrote eight theory papers about it. He resigned from the American Physical Society after their refusal to publish his papers. He felt that cold fusion research was being suppressed and academic freedom violated. He wrote: "The pressure for conformity is enormous. I have experienced it in editors’ rejection of submitted papers, based on venomous criticism of anonymous referees. The replacement of impartial reviewing by censorship will be the death of science."
Schwinger died of pancreatic cancer. He is buried at Mount Auburn Cemetery; is engraved above his name on his tombstone. These symbols refer to his calculation of the correction ("anomalous") to the magnetic moment of the electron.